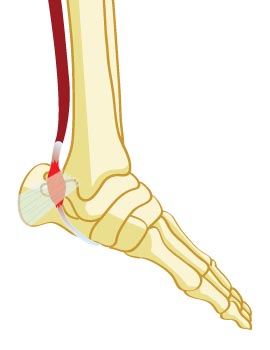
 The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons in the leg. The posterior tibial tendon attaches the calf muscle to the bones inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support the foot while walking.
The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons in the leg. The posterior tibial tendon attaches the calf muscle to the bones inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support the foot while walking.
A tremendous amount of tension and stress is placed on this tendon with every step, as it helps to maintain and recreate the arch of the foot. The amount of stress on the tendon varies from one person to the next—depending on the shape of their feet (flatfoot versus a very high arch). There are more occurrences of posterior tibial tendonitis in people with flat feet, but has the possibility of affecting anyone.
Most commonly, patients with posterior tibial tendonitis complain of pain inside of the foot and ankle, mostly caused by a recent ankle sprain—although some have reported no injury. The arch of the foot can flatten. As the foot flattens, the toes begin to point outwards as a result of the posterior tibial tendon not being able to do its job.
Most patients can be treated without surgery, using orthotics and braces. If orthotics and braces do not provide relief, surgery can be an effective way to help with the pain. Surgery might be as simple as removing the inflamed tissue or repairing a simple tear. However, more often than not, if surgery is very involved, many patients will notice some limitation in activity after surgery.
DON’T BACK DOWN
Ice and compression are always the first steps when dealing with any injury, whether it’s chronic or acute. Inflammation decreases blood flow which increases healing times.
 Crutches! With any foot/leg injury people are instructed to use crutches. The same applies for a tendon injury. Staying off your foot will help prevent re-injury and speed up healing times.
Crutches! With any foot/leg injury people are instructed to use crutches. The same applies for a tendon injury. Staying off your foot will help prevent re-injury and speed up healing times.
 Pain killers should only be used when not active. You need to tough it out during the day so your body can tell you when you when you’re hurting yourself. You run the risk of hurting yourself really badly if you take pills to numb the pain, because you won’t know what you’ve done to damage yourself until the pain killers wear off.
Pain killers should only be used when not active. You need to tough it out during the day so your body can tell you when you when you’re hurting yourself. You run the risk of hurting yourself really badly if you take pills to numb the pain, because you won’t know what you’ve done to damage yourself until the pain killers wear off.
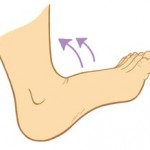 Stretch only if your body tells you it’s okay. Remember that stretching should feel good, and shouldn’t be painful. Pain means that you’re re-injuring yourself and you need to take a step back.
Stretch only if your body tells you it’s okay. Remember that stretching should feel good, and shouldn’t be painful. Pain means that you’re re-injuring yourself and you need to take a step back.
Heat to stimulate blood flow. Optimal blood flow is imperative for quick healing. Once the inflammation is down, the paths are cleared for nutrient rich blood to invade the injured area, helping speed up recovery times.
SURGERY
If all non-surgical methods fail, there are surgical options to help with treatment, depending on your case.
- Tenosynovectomy – in this procedure, the surgeon will clean away (debride) and remove (excise) any inflamed tissue surrounding the tendon.
- Osteotomy – This procedure changes the alignment of the heel bone (calcaneus). The surgeon may sometimes have to remove a portion of the bone.
- Tendon transfer – This procedure uses some fibers from another tendon (the flexor digitorum longus, which helps bend the toes) to repair the damaged posterior tibial tendon.
- Lateral column lengthening – in this procedure, the surgeon removes a small wedge-shaped piece of bone from either your hip or that of a cadaver and places it into the outside of the calcaneus. This helps realign the bones and recreates the arch.
- Arthrodesis – this procedure welds (fuses) on or more bones together, eliminating movement in the joint. This stabilizes the hindfoot and prevents the condition from progressing further.