When it comes to Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD), there are a number of different surgical options. Surgery for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction should only be considered if conservative treatments have failed to help. In most cases, conservative treatment methods for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction are successful. Ask your doctor if surgery is right for y ou.
ou.
Calf Muscle Lengthening
If you’re having issues with ankle movement, this procedure may be suitable for you. Calf Muscle Lengthening is also referred to as a “Gastrocnemius Recession”. It will help prevent flattening of the foot and may be performed along with other procedures to correct additional issues.
 Tendon Cleaning
Tendon Cleaning
This procedure is also called a Tenosynovectomy, as it involves the removal of the inflamed synovium, which is the membrane surrounding the tendon. A Tenosynovectomy can help to reduce your pain and swelling. It’s usually performed for more mild cases of PTTD and is another surgery that may be performed at the same time as other procedures.
Tendon Transfer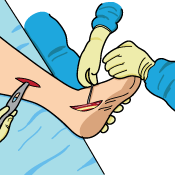
In a tendon transfer procedure, the damaged portion of the Posterior Tibial Tendon is removed and replaced with healthy tissue. This tissue will likely be taken from another area of your foot and grafted to the part of your tendon that’s remaining, to try and restore the tendon back to normal.
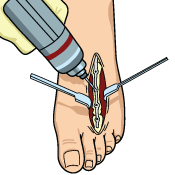 Osteotomy
Osteotomy
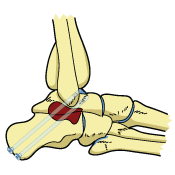
Osteotomy is usually performed in more serious cases of PTTD, where there is severe flattening of the foot. In this procedure, the goal is to try to restore the arch. This is usually done by making cuts in the bone and possibly using bone grafts. A tendon graft may also be done to further correct the Posterior Tibial Tedon Dysfuction.
Arthrodesis
If the foot is stiff, bone and tendon grafts may not be successful. This is where arthrodesis (joint fusion) comes in. This is another procedure that is typically designed for serious cases of PTTD. By fusing the joints in the foot, the surgeon attempts to restore the arch and realign the foot.