What is Sinus Tarsi Syndrome?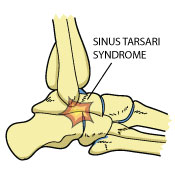
Sinus Tarsi Syndrome occurs when the soft tissue in the sinus tarsi area of your ankle becomes inflamed. The sinus tarsi is a bony space on the outside part of the ankle, located between the ankle bone and the heel bone. This area is also known as the subtalar joint. If not treated promptly, this condition can cause chronic pain.
 Causes
Causes
Sinus Tarsi Syndrome is usually caused by instability of the subtalar joint caused by an ankle sprain, repetitive strain injury, or a biomechanical issue with the foot. People with flatfoot and people who overpronate are at higher risk of developing Sinus Tarsi Syndrome because of the excess pressure that is placed on the sinus tarsi region. Ballet dancers and baseball pitchers are also at greater risk because of the way their feet are positioned during certain movements.
Signs & Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of Sinus Tarsi Syndrome include:
- Pain in the sinus tarsi area (especially with ankle movement)
- Ankle instability
- Ankle stiffness (worse in the morning, gets better as the day goes on)
- Tenderness in the sinus tarsi area
Treatment Options
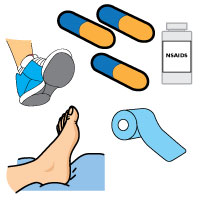 RICE – Rest, Ice, Compression & Elevation are effective at bringing down the swelling and controlling the pain associated with Sinus Tarsi Syndrome.
RICE – Rest, Ice, Compression & Elevation are effective at bringing down the swelling and controlling the pain associated with Sinus Tarsi Syndrome.
NSAIDs – Aleve and Advil are two examples of NSAIDs that will help with the pain and inflammation of your Sinus Tarsi Syndrome.
Physical Therapy – Stretching exercises, taping and other modalities used in physical therapy may work to manage your symptoms.
Proper Footwear – If you have Sinus Tarsi Syndrome, you need to avoid open-backed shoes. Wear shoes that provide your foot and ankle with comfortable support, and you may notice an improvement in your condition.
Surgery – Most cases of Sinus Tarsi Syndrome do not require surgery and can be treated with conservative modalities. If your Sinus Tarsi Syndrome does not seem to respond to conservative treatments, surgery is an option.