What is Os Trigonum Syndrome?
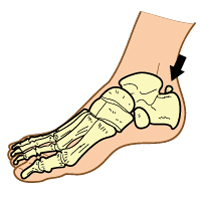 The Os Trigonum is an extra bone at the back of the ankle that is present at birth, which only a small number of people have. Many people with this extra bone will never know they have it, since they will not experience any issues related to it. People with an Os Trigonum that do activities involving repetitive plantar flexion (when the toes are pointing downwards) can develop Os Trigonum Syndrome (also known as posterior talar impingement). Os Trigonum Syndrome can also develop in people with an Os Trigonum who experience an ankle injury.
The Os Trigonum is an extra bone at the back of the ankle that is present at birth, which only a small number of people have. Many people with this extra bone will never know they have it, since they will not experience any issues related to it. People with an Os Trigonum that do activities involving repetitive plantar flexion (when the toes are pointing downwards) can develop Os Trigonum Syndrome (also known as posterior talar impingement). Os Trigonum Syndrome can also develop in people with an Os Trigonum who experience an ankle injury.
Os Trigonum Syndrome is often mistaken for Achilles Tendonitis.
Cause
 When someone with an Os Trigonum has their toes pointed downwards, they can experience what’s called a “nutcracker injury”. This happens when the Os Trigonum is trapped between the ankle bone and the heel bone, causing the surrounding soft tissue to become irritated and inflamed. Athletes most at risk of developing Os Trigonum Syndrome include ballet dancers, soccer players, runners and football players.
When someone with an Os Trigonum has their toes pointed downwards, they can experience what’s called a “nutcracker injury”. This happens when the Os Trigonum is trapped between the ankle bone and the heel bone, causing the surrounding soft tissue to become irritated and inflamed. Athletes most at risk of developing Os Trigonum Syndrome include ballet dancers, soccer players, runners and football players.
Signs & Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of Os Trigonum Syndrome include:
- Pain & swelling in the back of the ankle
- Tenderness in the affected area
- There may be a lump at the back of the ankle
Treatments
 RICE – Rest, Ice, Compression & Elevation will help control your pain and swelling, as well as prevent further inflammation.
RICE – Rest, Ice, Compression & Elevation will help control your pain and swelling, as well as prevent further inflammation.
Painkillers – NSAIDs like Aleve and Advil will work to relieve your pain and bring down the internal inflammation.
Physiotherapy – A program of stretching and strengthening exercises may help to relieve pressure from the Os Trigonum.
Cortisone Injections – Cortisone can be injected into the back of your ankle to temporarily relieve pain and inflammation. However, there are various risks associated with cortisone shots, such as bone death, nerve damage, skin discoloration and rupture of the tendon.
Surgery – In most cases of Os Trigonum Syndrome, surgery is not required. Surgery should only be considered if conservative treatment options have not been successful. Surgery for Os Trigonum Syndrome involves the removal of this extra bone, as it’s not required for the foot to function normally.